
Threat Hunting: Identifying Risks in Remote Control Software

Developing a comprehensive detection strategy to distinguish between malicious and legitimate utilization of Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software is of paramount importance. This is especially crucial considering the widespread use of RMM tools among both cyber adversaries and IT administrators.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the National Security Agency (NSA) issued an advisory about the malicious use of RMMs. SCATTERED SPIDER, Royal, and Conti are just some of the big-name adversaries that perform lateral movement and establish command and control (C2) via legitimate RMMs.
In December 2020, adversaries successfully compromised SolarWinds, gaining access to the update infrastructure for its Orion IT management software. They proceeded to distribute malicious updates to thousands of SolarWinds customers, resulting in a significant breach that impacted organizations well into 2021.
Furthermore, in July 2021, adversaries exploited vulnerabilities in the Kaseya VSA IT Management software. This campaign was orchestrated with the ultimate goal of deploying Sodinokibi ransomware, also known as REvil, affecting multiple organizations in a high-profile incident. According to Red Canary Threat Intelligence, NetSupport Manager has made it into their top 10 list for July.
Understanding RMM Tools
A Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tool is a software solution that empowers IT professionals and Managed Service Providers (MSPs) to remotely oversee and maintain IT assets. Key functionalities include remote control for troubleshooting, system health monitoring, software update automation, asset management, security enhancement, and reporting. RMM tools play a pivotal role in efficient IT management, enhancing reliability, and minimizing downtime. They are available in various forms, ranging from software applications to cloud-based platforms, catering to diverse organizational requirements.
I've observed RMM tools being used for diverse purposes, including system updates, asset inventory management, software deployment across multiple workstations, resolution of endpoint issues with privileged command-line access, scheduling of maintenance tasks, and comprehensive network and endpoint monitoring.
The Significance of Threat Hunting in Remote Access Software
Why should you proactively search for threats related to Remote Access Software? MITRE has extensively documented that numerous Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) groups have exploited remote access software to maintain a low profile and persistence within compromised networks. Hunting for threats associated with Remote Access Software holds critical importance for several reasons:
- Detection of Malicious Use: Adversaries often exploit legitimate desktop software, including remote access tools, to establish stealthy and persistent footholds within compromised networks. By continuously monitoring for suspicious activities linked to these tools, organizations can detect and mitigate potential threats at an early stage.
- Identifying APT Activity: As you mentioned, various Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) groups have been known to exploit remote access software. These groups often use these tools to conduct reconnaissance, move laterally, and exfiltrate data. Detecting such activity can be a crucial part of threat intelligence and defense.
- Supply-Chain Attack Prevention: Staying vigilant regarding remote access software is imperative for identifying potential supply-chain attacks. Incidents like the SolarWinds breach have highlighted how adversaries can compromise trusted software vendors to infiltrate multiple organizations. Monitoring for suspicious activity within remote access software can help uncover such attacks before they inflict substantial damage.
- Early Threat Detection: Identifying anomalies or unusual behavior within remote access software can lead to early threat detection. This allows security teams to respond quickly, potentially preventing data breaches or other damaging consequences.
- Compliance and Security Standards: Many security regulations and standards, such as PCI DSS and NIST, require organizations to monitor and secure remote access tools. Proactively hunting for threats related to these tools can aid in compliance efforts.
In conclusion, proactively hunting for threats related to Remote Access Software is a critical security measure. It aids organizations in detecting, mitigating, and preventing various types of cyber threats, ranging from APT activity to supply-chain attacks. This practice is an integral part of a robust cybersecurity strategy.
Initiating the Hunt
Conducting a threat hunt on RMM software can indeed be a challenging endeavor. Establishing a baseline for your environment before embarking on this journey is a prudent approach. To create this baseline, consider the following questions:
- What RMM Software Do Your IT Staff Use?
- Identify the specific RMM tools in use within your organization. This could include tools like SolarWinds, Kaseya, TeamViewer, or any others. Knowing which tools are authorized for use is crucial for spotting any unauthorized or suspicious activity.
- What Are Your General Office Hours?
- Determine the typical working hours for your organization. This information helps establish when normal network activity should occur. Any activity outside these hours may be considered unusual and warrant investigation.
- How Do You Connect to the Corporate Network? Does That System Generate Authentication Logs?
- Comprehend the various methods employees utilize to connect to the corporate network. This might encompass VPN connections, remote desktop sessions, or alternative forms of remote access. Ensure that systems responsible for authentication generate logs. These logs serve as valuable assets for monitoring and identifying potential threats.
By addressing these questions, you'll establish a solid foundation for comprehending the normal patterns of RMM software utilization, network connectivity, and authentication within your organization. This baseline equips you to more effectively detect and respond to anomalies or potential threats during your threat-hunting endeavors.
Identifying RMM Software in Your Environment
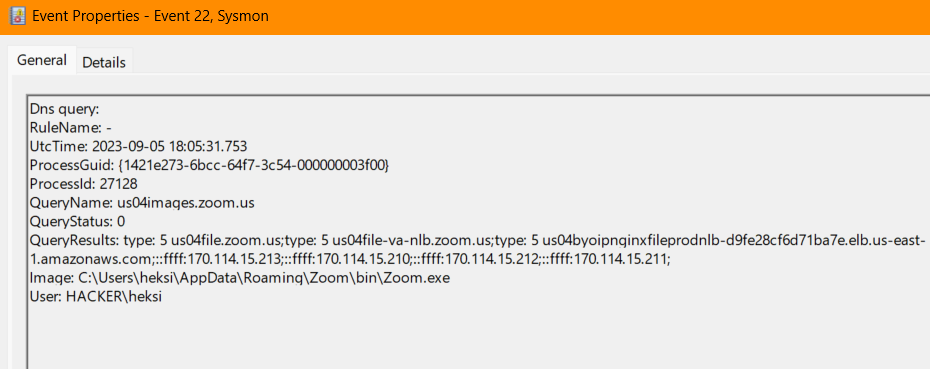
Numerous remote access software solutions are available, all of which share the common trait of creating processes when running on a system. RMM software process names tend to remain relatively consistent. Another effective method for detecting RMM software usage involves monitoring DNS Query events.
In environments where Sysmon is installed, it is possible to search for multiple Sysmon events related to RMM Software. Sysmon Event ID-1, for instance, provides comprehensive information about newly created processes, including full command line details. Event ID-3 reveals the ImageName, which contains the application name, while Event ID-22 captures DNS query events, which is particularly useful for identifying RMM Software domains.
While many RMM software solutions are available, the examples below offer a starting point. In your central log management solution, filter for 4688 event logs. Here are some illustrative examples:
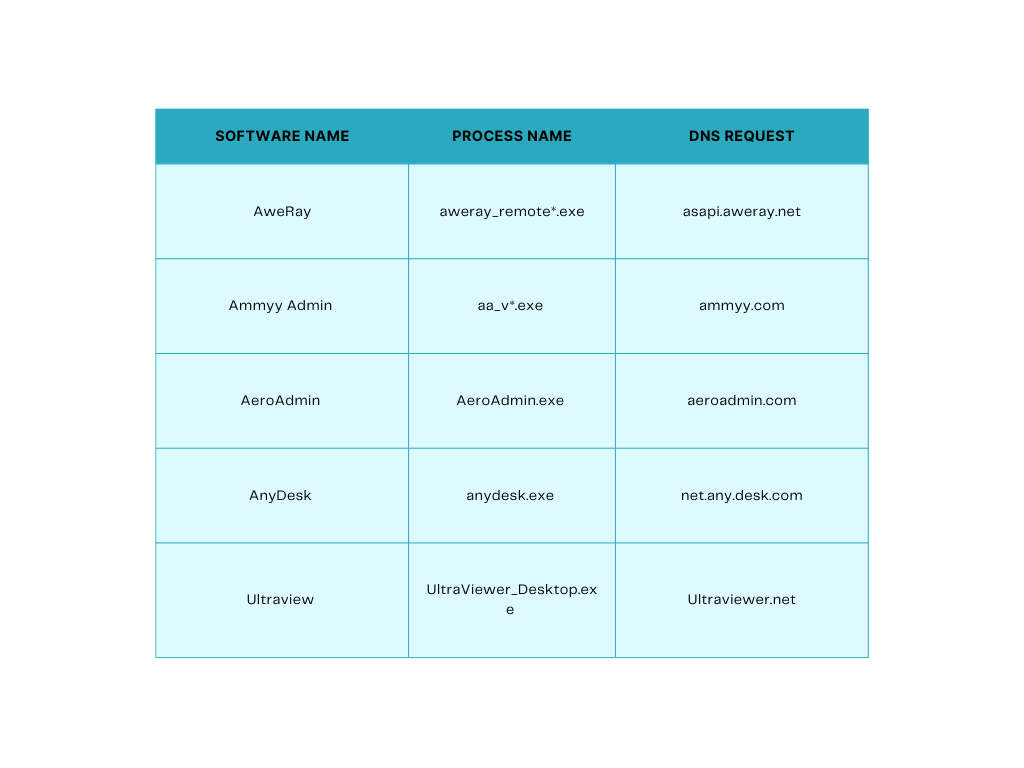
Sysmon Event ID-1: The process creation event provides extended information about a newly created process. The full command line provides context on the process execution. In the following, we can identify Teams.exe.
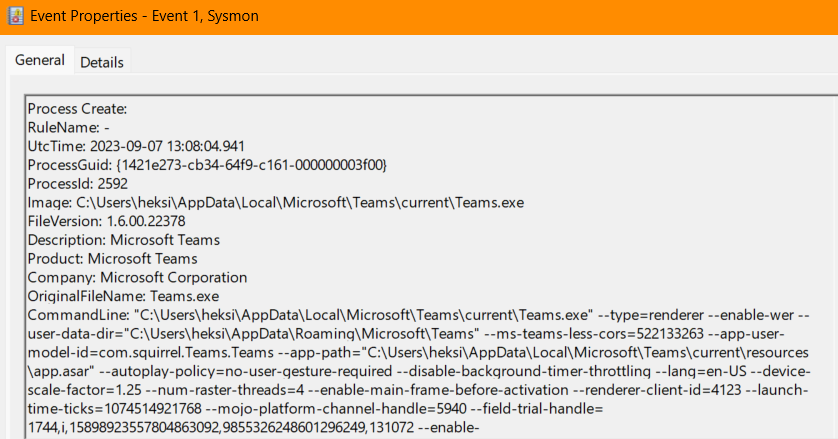
Sysmon Event ID-3 This event provides essential information about newly created processes, including the ImageName, which typically contains the application name or executable filename.
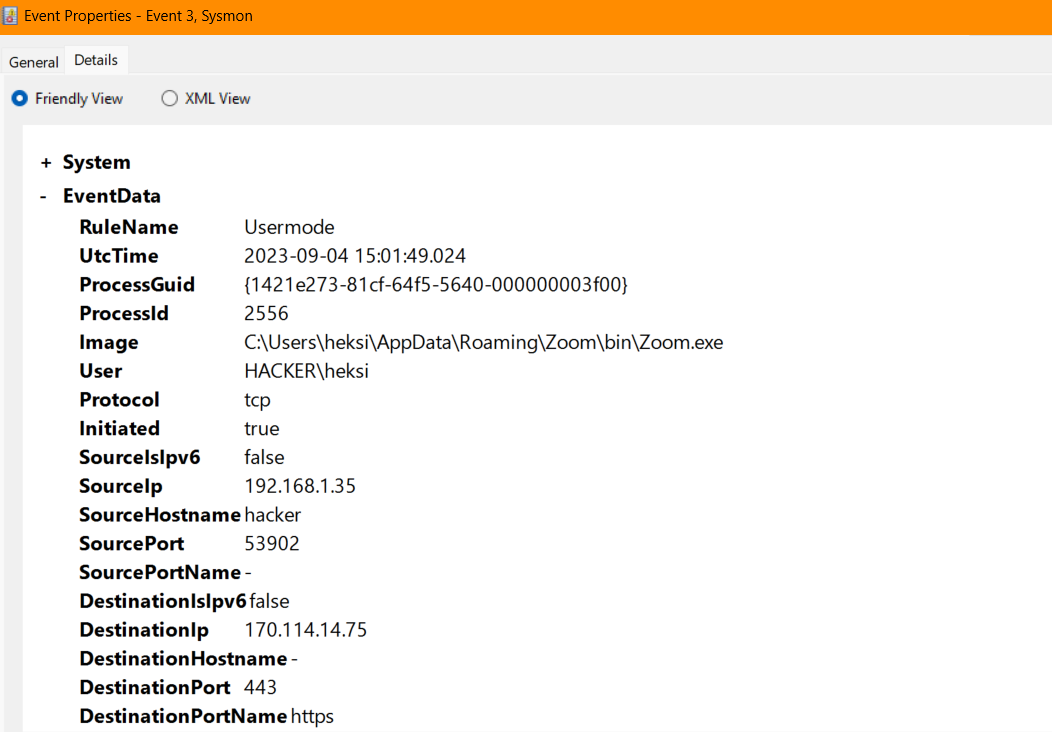
Sysmon Event ID-22 This event, which captures DNS query events, is indeed valuable when monitoring RMM software usage and potential security threats. RMM software often queries specific domains as part of its normal operation.
By effectively monitoring these events and processes, you can enhance your organization's ability to detect and respond to potential threats associated with RMM software.

 En
En  de
de